- Elastic Beanstalk is a developer centric view of deploying an application on AWS
- It uses all the component's we've seen before: EC2, ASG, ELB, RDS, etc...
- But it's all in one view that's easy to make sense of!
- We still have full control over the configuration
- Beanstalk = Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Managed service
- Instance configuration / OS is handled by Beanstalk
- Deployment strategy is configurable but performed by Elastic Beanstalk
- Capacity provisioning
- Load balancing & auto-scaling
- Application health-monitoring & responsiveness
Responsibility
- Just the application code is the responsibility of the developer
Architecture
- Three architecture models:
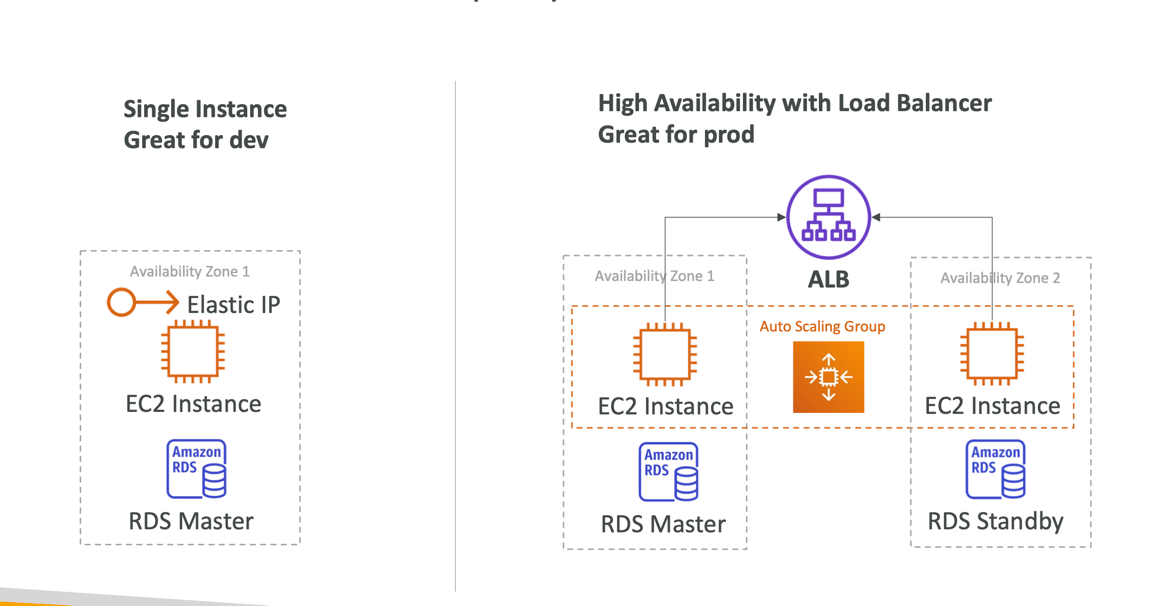
- Single Instance deployment: good for dev
- ELB + ASG: great for production or pre-production web applications
- ASG only: great for non-web apps in production (workers, etc..)
Beanstalk
- Health agent pushes metrics to CloudWatch
- Checks for app health, publishes health events
Elastic Beanstalk – Components
- Application: collection of Elastic Beanstalk components (environments, versions, configurations, …)
- Application Version: an iteration of your application code
- Environment
- Collection of AWS resources running an application version (only one application version at a time)
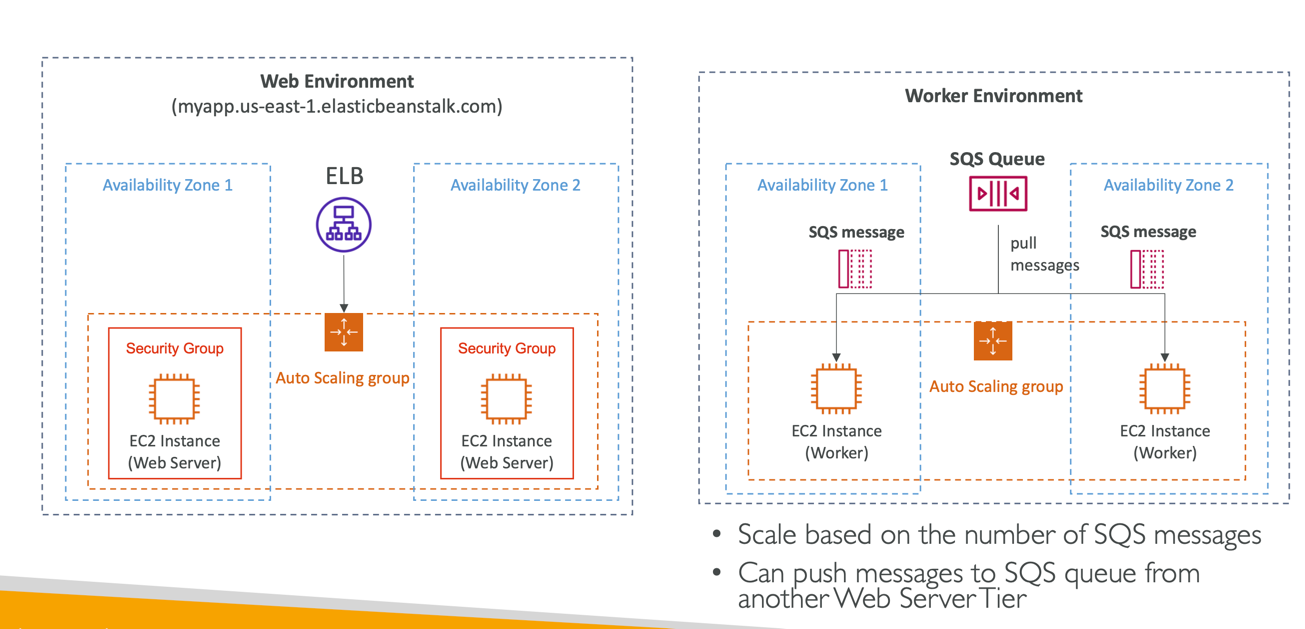
- Tiers: Web Server Environment Tier & Worker Environment Tier
- You can create multiple environments (dev, test, prod, …)
Web Server Tier vs. Worker Tier
Elastic Beanstalk Deployment Modes